Dragonfly is a carnivorous winged insect belonging to the arthropod, the order of dragonfly. Of these, 608 species have died out, and the remaining 5899 have settled on the planet at the moment.
There are 3 suborders of dragonflies:
- diverse wings;
- winged;
- anisozygoptera.
Origin of the species
Dragonflies are an ancient group of arthropods. The first dragonflies lived on the planet back in the Carboniferous period in the Paleozoic era. The origin is associated with giant dragonfly insects meganeuvers. Those, in turn, were large arthropods with a wingspan of up to 0.66 meters. They are considered the largest arthropods of the time. Subsequently, it was they who became the descendants of Kennedyina, Ditaxineurina, already living in the Triassic period of the Mesozoic. These arthropods also differed in large sizes, span up to 90 mm. When the animals rested, the wings hid under the abdomen.

In those days, insects had a well-developed basket for fishing. They grabbed her victims. The next descendants of the meganeuvres living in the Jurassic period are Lestomorpha, Libellulomorpha, whose larvae are capable of developing in water. Their aircraft has changed significantly, becoming more advanced. Descendants of the Meganeurins gradually settled throughout the planet.
At this time, the descendants of the superfamily Calopterygoidea radically changed. Their wings became already leveled in size. The Cretaceous era took away many suborders of insects, and in the Cenozoic era, modern suborders of dragonflies can be seen. In Neocene, dragonflies ceased to differ from modern ones.
Video: dragonfly
Description, appearance and features
These insects are easily distinguished from other arthropods with the naked eye. In this case, the color of animals can radically vary. The most expressive parts of the body of the insect are:
- Large head with expressive eyes.
- A little body of bright colors, sometimes brilliant.
- Thoracic part.
- Transparent wings of various shades.

Depending on the species, animals come in different sizes. The smallest dragonflies are considered to be up to 1.5 cm long. The largest representatives grow up to 10 cm. A large head is able to rotate 180 degrees. Large eyes consist of thousands of ommatidia, whose number can vary from 10,000 to 27.5 thousand.
It is proved that the lower ommatias reproduce only colors, and the upper ones determine the shape of objects. This feature allows the dragonflies to navigate perfectly in flight and catch prey. On the crown of the dragonfly there is a slight swelling, on which are three additional eyes. Dragonflies also have an awl-shaped antennae, they are short and consist of about four to seven segments.

Interesting fact: Dragonfly eyes have a complex structure. They consist of 30 thousand ommatia that can instantly navigate in space.
Powerful jaw apparatus formed by unpaired lips. At the same time, the lower lip consists of three lobes covering powerful jaws. The upper lip in the form of a small plate, elongated across, covers the upper jaw. The insect is able to catch and chew food during the flight due to the difference in the size of the upper and lower lips.
Interesting fact: Dragonflies hunt for other insects and avoid collisions thanks to a viewing angle of almost 360 degrees.
The thoracic part of three departments: the front, middle, back, with a pair of limbs on each. The wings of the animal are also located on the last two sections. The front section is separated from the middle, which, together with the rear, are fused together, forming synthorax, which is perceived as a chest.

The chest is flattened on the sides, and the dorsal part is slightly pushed back. The middle part of the chest is above the back, so the wings are entangled behind the legs.The front of the back is divided into three sections. On the average of them is a dent. The segments on which the wings grow are hypertrophic pleirites.
Interesting fact: dragonflies are endurance. Red strollers are champions in migration. They overcome great distances during flights - more than 6.5 thousand km.
Dragonfly wings are practically colorless and consist of a pair of layers of chitin formed by the venation system. The cores are superimposed on each other in such a way that they seem to be a single network. The system is complex and dense, each dragonfly squad has a unique mesh of wings.

The abdomen of dragonflies is rounded elongated. Some species have a flat abdomen. In all species, it is the abdomen that is the greater part of the body. The abdomen is divided into 10 segments. From the sides of the abdomen, there are pleural membranes that allow the insect to bend.
In addition to the last two, each segment contains sigma. At the tip of the abdomen are anal appendages, the number of which varies in females, males. Females have two, and males have three to four. The female genitals are located at the end of the abdomen, while in males the compilation organ is located on the second abdominal segment. The hole for the withdrawal of seed in males is located on the tenth abdominal segment. Insects have strong and well-formed limbs, consisting of the femoral, pelvic, lower leg parts and the veil with legs. There are spikes on each leg.
How to distinguish between a male and a female dragonfly?
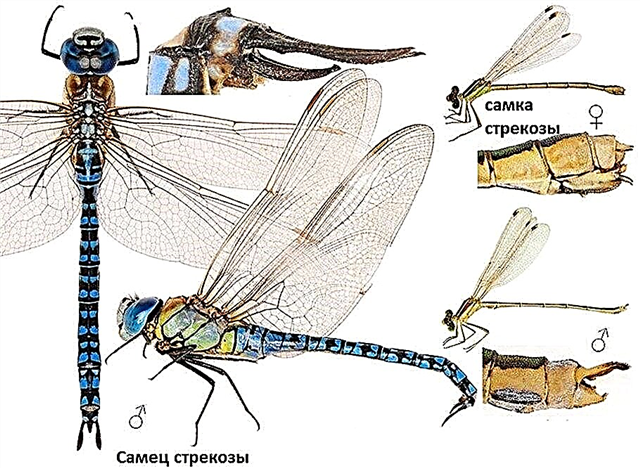
Insects are characterized by sexual dimorphism. These are the external differences between males and females, which are clearly visible especially in dragonflies. Dimorphism is important for the reproductive behavior of dragonflies. Amazing but insect color changes throughout life, the final establishment of color is noted at adulthood.
There are different options for sexual dimorphism of dragonflies. Some species are distinguished by large females and small males, while others are the opposite. In insect families, certain tendencies of dimorphism are also noted. Beauties are distinguished by large males, and arrows by large females. The color of individuals is considered an important sign of sexual dimorphism. The pattern on the wings is also a sign of sex.
Sometimes polymorphism is observed in insects, that is, the presence of certain forms of the same species, which differ in color. In such cases, the color is not associated with dimorphism.
Area - where does the dragonfly live?
Dragonflies are spread all over the world. The only place where dragonflies cannot be found is Antarctica. Most of the species are in the Indo-Malay region. There are approximately 1664 species of animals. 1640 species are widespread in the neotropics, 889 in the afrotropics, and 870 species in Australia and the region. In temperate regions, fewer species live. This is because insects prefer warm, moist conditions.
Eggs are laid in water tanks, rivers. Depending on the species, they are especially relevant to the choice of breeding site. Dragonflies Pseudostigmatinae prefer small water reservoirs, while other species can only breed in rivers or large lakes. Larvae are constantly in the water; they can stay there for up to two years. Individuals who learn to fly gradually fly away from the place of birth over long distances, migrating.
Habitat

Insects prefer warm areas, while spreading to areas where negative temperatures are not maintained for more than three months per year. The animal’s lifestyle is amphibious, that is, offspring are raised in water, and adults live in a land-air environment.
Dragonflies are fast, easily maneuvering. Air for them is considered a home. Having occupied certain territories, dragonflies will protect them from enemies to the last, even in the person of relatives.
How many dragonflies live?
Insects live for several months. Moreover, the entire development of dragonflies takes more than one year. Hatching under water larvae live there from several months to four years. They develop, hunt and hide from enemies. Gradually, dragonflies molt and grow, learn to fly. Adults leave water bodies and begin migration.
Dragonflies are special insects. For rebirth in adults, they do not need pupae or cocoons. After the appearance of an adult dragonfly dries for a while from the water and begins its flight. A few hours after growing up, the dragonflies begin to hunt for winged insects, gradually adapting to new conditions. At this stage of development, the insect is strongly affected by ambient temperature and climate. In warm conditions without rainfall, dragonflies live up to six months, while in the cold they survive for several weeks.
How do dragonflies hibernate?
All winter, dragonflies are under water in the larval stage. The structure of the larvae provides for the presence of gills that breathe under water. In spring, the larvae mature, crawl to the surface, dry out and begin hunting.
What does a dragonfly eat?

Dragonflies are predators, therefore they feed on the majority of insects living in the air. Mostly their diet consists of midges, mosquitoes, various flies, arthropods. In the larval stage, small fish or the like are eaten.
Subtypes are divided according to the method of hunting:
- Free hunters - fly high. They have strong developed wings that allow maneuvering on the upper tiers. Sometimes they hunt in a flock, but more often all alone, flying at a distance two to nine meters.
- Free flying, hunting in the middle tier. Do not fly overboard two meters high. They are constantly looking for food, sometimes relaxing on plants.
- Lurking - hunt from ambush, waiting for prey.
- Dragonflies also live in the lower tier. They hunt in grass thickets, catching insects on plants. They feed while sitting on the grass, not in flight.
Features of character and lifestyle

In Russia, dragonflies are found from mid-spring to mid-autumn. In warm regions, insects are found throughout the year. Insects lead a daily lifestyle, showing great activity on warm sunny days.
In the mornings, dragonflies bask under the sun, resting on stones, grass or trees. At noon, they take the “reflection” position, reflecting the sun's rays with the tip of the abdomen. Thus, the animal does not overheat. Hunting takes place in the evenings and in the morning. Species are more active during dawn. At night, dragonflies rest alone in the undergrowth.
Social structure and reproduction

Animals undergo three processes of transformation: egg-larvae-adults, that is, adults. Dragonflies lay eggs several times a year. Mating takes place on the fly, males perform mating dances, showing various things in the air. In one clutch there are up to 500 eggs. Only a few survive, avoiding death from fish or birds.
Larvae become adults only after a year, sometimes the process drags on for several years. The size of the new larvae is approximately 1 mm; molting begins almost immediately; they feed on their own and hunt under water.
Interesting fact: Certain species lay eggs in salt water. Dragonflies are exceptional insects that can live in the ocean.
The natural enemies of dragonflies
Enemies of dragonflies are considered large predatory insects, animals and people. Eggs feed on fish, bird larvae. Human activity leads to the pollution of natural bodies of water. Dragonflies gradually die out. Dragonflies can also become victims of insectivorous flowers. It’s difficult to catch an insect, but harder to catch it by surprise.
Interesting fact: dragonflies possess strong, strong jaws, capable of grabbing prey on the fly.
Types of Dragonflies
It is possible to meet these insects all over the planet, therefore they are very diverse in their appearance and structure. Some species of dragonflies are studied only by finds in a particular area, and some became known thanks to single samples. A significant part of the species has not yet been studied by researchers. In 2013, there were 6,650 species of dragonflies in the world, along with 608 fossils. Each year, the number increases by several dozen. In two years of research, the number of living species has risen to 5899.
Graceful arrow

They live in the European part of the continent. Small size - up to 3.5 cm and with a thin elongated abdominal part. The wings are transparent, limbs and body are black with a characteristic pattern of blue, black or green-yellow shades.
Beauty Girl - Dragonfly

Relatively large insects, up to 50 mm long. Males are bluish or metallic in color, females with smoky transparent sinewy wings. Most often found in Asia, less commonly in southern Siberia.
Interesting fact: dragonflies tear wings off of their victims, depriving them of the opportunity to escape. At the same time, dragonflies are not able to harm people due to the fact that they can not bite through the skin.
Lyutki

Lute dull - common in the European part of Russia. Mostly settle in shallow water, have a metallic greenish coloring. Can be of various colors and types.
Interesting fact: dragonflies fly great. Only some insects on the planet can compete with dragonflies in the beauty of flight. Two pairs of wings are arranged so that they can move regardless of the others. Dragonflies can dramatically change direction in a split second.
Ordinary grandfather

Dragonflies of medium size - no more than 50 mm. With large green eyes and chest, painted with black oblique stripes. The hue of the chest is yellow, the abdominal part is black with small yellow spots on the sides. Distributed in Central Asia, the South Caucasus.
Interesting fact: Dragonflies can live underwater for two years. Insects lay eggs under water, and hatched offspring can spend up to two years there. They adapt to underwater life, learn to hunt and hide from enemies. Dragonflies can also feed on larvae of their own kind.
Flat bellies

Flat bellies are a fairly common family of dragonflies of various colors. Most often, dragonflies are brown-yellow with green or blue stripes, sometimes with reddish ornaments.
Interesting fact: there are dragonfly reserves around the world. Since human activity has a detrimental effect on insect populations, protected areas have been identified. The first such reserve was opened in Britain in 2009.
Population and species status

Dragonflies are common throughout the globe. As early as 2013, there were approximately 6,650 species of animals on the planet. At the moment, indicators have increased significantly. Researchers are constantly finding new species. However, at the moment, some species of dragonflies can disappear forever. This is due to constant human pollution of the environment.
At the end of 2018, more than three hundred species were threatened with extinction. One species, Megalagrion jugorum, is considered extinct. About 10% of all animal species are endangered. Insects are important for determining the state of natural water bodies. They prey on pests, react strongly to changes in water quality. To preserve the species, you should be careful about nature.
Dragonfly guard

Animals occupy an important place in the functioning of the ecosystem. They destroy pests, are considered food for birds and fish, as well as mammals and other insects. In addition, by the state of dragonflies it is possible to determine the state of water in the region. Dragonflies begin to die out where water bodies are contaminated.
Many species are threatened with extinction due to constant pollution of water bodies.The established Insect Protection Society tracks population numbers.
Economic value
Like many dragonfly predators, they are useful and at the same time harm the economy. Adult insects kill pests, but larvae often eat the necessary species of fish in the lakes.
Also, larvae are considered to be carriers of prostogonimosis of birds, as they are hosts of parasites. In such cases, domestic birds such as chickens, turkeys and geese are affected. Often trematodes are found in wild animals. The feces of sick birds falling into the water are eaten by mollusks, where miracidia begins to develop. They gradually turn into sporocysts, redia, after which they leave the mollusks and again find themselves in dragonfly larvae. The process is repeated again and again when the birds destroy the larvae.
Dragonfly study
Odonatologists - people specializing in the study of dragonflies, study varieties of these insects in the laboratory. Even at the border of the last and present century, more than seven hundred scientists from 70 countries worked on the study of dragonflies. In 1971, a odonatological society was established, headquartered in the Netherlands.
In 1957, the oldest odonatological society also appeared in Japan. In European countries, dragonflies were thoroughly studied and magazines were published about them. A large scientific school of odonatologists was also created in Russia, the writings of the representatives of which served science by discovering fundamental spatial features, as well as the zoogeographic distribution of insects across the planet.
For 36 years - 1971-2005, more than 14 thousand scientific publications on the study of dragonflies have been published worldwide. Since 2010, congresses of odonatologists gather around the world. Currently, there is the World Association of Dragonfly Researchers in the world, giving grants to promising odonatological studies.
Interesting dragonfly video












